In horticulture and controlled environment agriculture (CEA), ensuring high-quality water is vital for optimal plant growth. Reverse osmosis hydroponics plays a crucial role in this by removing contaminants and providing clean, nutrient-rich water.
By ensuring the purity of water used in irrigation and hydroponic systems, reverse osmosis (RO) plays a crucial role in promoting robust plant growth, preventing disease, and supporting sustainable agricultural practices.
Let’s explore how RO technology enhances CEA water quality, ensuring optimal conditions for thriving crops.
What is Reverse Osmosis (RO)?
Reverse osmosis is a water purification technology that uses a semipermeable membrane to filter out impurities. This process ensures that only water molecules pass through, leaving contaminants like salts and minerals behind.
For reverse osmosis systems to perform optimally, especially in industrial wastewater treatment, a critical pre-treatment phase is necessary. This phase protects the membrane from organic fouling, mineral scaling, and chemical degradation. Advanced pre-treatment technologies are incorporated into customized RO systems to ensure the highest removal rates of contaminants.
The high-quality water produced by RO systems is indispensable in irrigation and hydroponic systems within controlled environment agriculture (CEA). By meticulously controlling mineral content and regulating pH levels, RO technology ensures that plants receive the purest water, fostering healthier and more vigorous growth. This makes reverse osmosis a cornerstone technology in achieving optimal plant health and productivity in CEA.
Importance of Water Quality in CEA
In controlled environment agriculture (CEA), water quality is paramount for healthy and productive plant growth. Clean, contaminant-free water is essential to avoid issues that can impede plant development and degrade growing conditions.
The water purification process often relies on reverse osmosis (RO), a method that filters water through a semipermeable membrane, allowing only water molecules to pass while blocking contaminants like ions, salts, and minerals. The result is pristine water for plants, free from impurities that might hinder their growth. Additionally, growers can integrate supplementary components to adjust the water’s nutrient concentration, ensuring optimal conditions for plant development.
High-quality CEA water treatment help solve critical issues like:
- Preventing Salt Buildup: Clean water prevents salt accumulation in the growth medium, which can hinder nutrient uptake and cause soil degradation. This ensures a healthier growing environment where plants can thrive.
- Improving Nutrient Absorption: Contaminant-free water enhances plants’ ability to absorb essential nutrients, promoting vigorous growth and development.
- Reducing Disease Risk: Pure water helps eliminate pathogens, reducing the reliance on chemical fertilizers and treatments and fostering healthier plants with heightened resilience against diseases and pests.
- Promoting Eco-Friendly Practices: By decreasing the need for chemical fertilizers and preventing soil salinity, clean water contributes to reducing agriculture’s ecological impact. This shift aligns with sustainable farming practices and helps shrink the overall environmental footprint of crop production.
- Conserving Water: Efficient water use, including potential reuse or treatment of water, is crucial. Judicious water management is particularly vital in water-scarce regions or areas where conventional irrigation methods are insufficient.
Ensuring high water quality in CEA is essential for optimal plant health and productivity. By providing pure, contaminant-free water, growers can create an environment where plants can flourish, leading to successful and sustainable agricultural practices.
How Does Reverse Osmosis Work?
Reverse osmosis (RO) stands as a cutting-edge wastewater treatment solution, harnessing membrane technology to effectively separate dissolved impurities from contaminated water. Operating under pressures ranging from 150 to 600 pounds per square inch (psi), RO systems utilize super thin membranes that act as barriers, allowing for the selective passage of water molecules while retaining the majority of dissolved materials. Playing a pivotal role by dividing the waste stream into a permeate stream (low concentration) and a concentrated stream (high concentration), particularly in one-stage systems. For advanced efficiency, two-stage systems can be implemented, where the concentrate stream undergoes treatment in a second RO system. The number of stages directly correlates with the system’s effectiveness in water recovery.
1. Pre-Filtration
The water from the source (usually tap water or well water) undergoes pre-filtration to remove large particles, sediment, and other impurities that might damage the RO membrane. This typically involves passing the water through a series of filters, such as sediment filters and activated carbon filters.
2. Pressure Boost
The pre-filtered water is pressurized to a level higher than the osmotic pressure of the contaminants. This pressure is necessary to overcome the natural osmotic pressure and force the water through the semipermeable membrane.
3. Reverse Osmosis Membrane
The heart of the reverse osmosis system is the semi-permeable membrane. This membrane allows water molecules to pass through while blocking the majority of contaminants, including salts, minerals, bacteria, and other impurities. The size of the pores in the membrane is extremely small, typically measured in microns, ensuring thorough purification.
4. Separation of Water and Contaminants
The pressurized water is forced through the RO membrane, leaving behind contaminants on one side of the membrane while allowing purified water to pass through to the other side. This separation is based on the principle of osmosis, where water molecules move from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration.
5. Reject Water Disposal
The concentrated solution containing the rejected contaminants, often referred to as reject water or brine, is directed to a drain. This is an essential aspect of the RO process, as it helps prevent the accumulation of concentrated impurities on the membrane surface.
6. Product Water Collection
The purified water, now free from the majority of contaminants, is collected for use in irrigation systems or hydroponic setups in controlled environment agriculture. This high-quality water is essential for preventing the build-up of salts and minerals in the growing medium and ensuring optimal nutrient uptake by the plants.
While reverse osmosis is highly effective in producing purified water, it’s essential to note that it also generates reject water, and the overall efficiency of the system depends on factors such as the quality of the source water and the type of membrane used. Proper maintenance and periodic monitoring of the system are crucial to ensure optimal performance in controlled environment agriculture.
Benefits of Reverse Osmosis in CEA
RO’s efficiency extends to water conservation, permitting only purified water to pass while managing the concentrated solution (brine) for potential reuse or treatment. This judicious use of water aligns with sustainable agricultural practices, especially vital in water-scarce regions or where conventional irrigation methods fall short. Ultimately, the integration of reverse osmosis systems is the foundation for ensuring water purity, precise nutrient control, and overall sustainability, fostering both the success and environmental conscientiousness of contemporary agricultural practices.
1. Irrigation
RO systems are used to purify water for irrigation purposes. By removing impurities, minerals, and salts, RO-treated water helps prevent the accumulation of these substances in the growing medium, promoting optimal plant growth and health.
2. Hydroponic Systems
Hydroponic systems, which involve growing plants without soil and using nutrient-rich water solutions, benefit from the use of RO water. The purified water ensures that the nutrient solution remains free from unwanted contaminants, allowing for precise control over the nutrient levels delivered to the plants.
3. Mineral and pH Control
RO technology enables growers to have better control over the mineral content and pH of the water used in CEA. This is crucial for maintaining the desired nutrient balance and pH levels in the growing medium, providing an ideal environment for plant growth.
4. Preventing Salt Buildup
The controlled removal of salts through RO helps prevent the buildup of salts in the root zone, which can negatively impact nutrient uptake by plants. This is particularly important in hydroponic and soilless growing systems.
5. Pathogen Prevention
RO systems effectively remove bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens from the water, reducing the risk of diseases that can affect plants in a controlled environment.
Overall, reverse osmosis contributes to the creation of a consistent and optimized growing environment. It gives growers precise control over water quality, promoting healthier plants and potentially increasing crop yields. It helps to extend the lifespan of irrigation and hydroponic systems by preventing clogs and damage caused by impurities in untreated water.
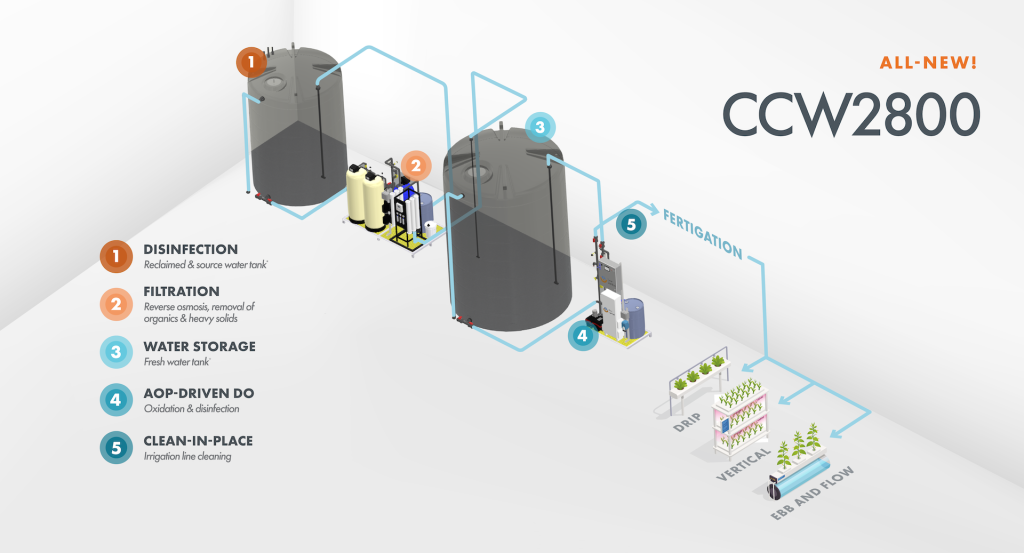
Combining RO, AOP & DO for Enhanced CEA Water Quality
In CEA, the synergy of Reverse Osmosis (RO), Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOP), and Dissolved Oxygen (DO) management is pivotal in creating Fertigation-Ready Water™ through efficient water reclamation. This integrated approach enhances water purification, ensuring removal of pollutants and control of microbial threats, while maintaining system efficiency. This combination not only improves water quality for plant growth but also optimizes it for fertigation, a key component in sustainable CEA practices.
How AOP Enhances the RO Process
Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) play a crucial role in augmenting the effectiveness of Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems within Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA). RO is known for its superior water purification, but it faces challenges in removing certain persistent organic pollutants and microbes. The incorporation of AOPs addresses these challenges, utilizing highly reactive hydroxyl radicals to break down resistant organic compounds. By integrating AOPs, not only are contaminants such as pesticides and pathogens effectively neutralized, but biofouling in RO systems is also prevented. This enhances both the longevity of the RO membranes and the overall efficiency of the water purification process.
How DO Enhances the RO Process
The maintenance of adequate dissolved oxygen levels is vital in RO systems, playing a key role in preventing microbial growth. High DO levels, facilitated by AOPs, help inhibit the formation of biofilms on RO membranes, a common issue known as biofouling. This microbial-induced fouling can reduce the efficiency and increase maintenance needs of RO systems. By ensuring sufficient dissolved oxygen in the system, CEA facilities can effectively control microbial contamination, further enhancing the durability and performance of RO units.
These enhancements in water treatment through AOP and DO management significantly boost the performance of RO systems, leading to more efficient and sustainable operations in CEA facilities. This combined approach ensures that the water is not just desalinated but also rigorously purified, meeting the high-quality standards required for successful plant growth in controlled environments.
Future Alignment: Reverse Osmosis in CEA
The integration of Reverse Osmosis (RO) and Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) emerges as a transformative solution in Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA), effectively addressing the intricate challenges associated with water quality and purification. RO stands as the foundation for high-quality water tailored to the precise conditions of CEA, adept at filtering contaminants, regulating mineral content, and preventing salt accumulation to foster optimal plant growth and overall agricultural productivity.
The incorporation of AOPs into the RO process is an additional layer of efficiency, addressing persistent organic pollutants and microbial threats that may elude conventional purification methods. AOPs generate hydroxyl radicals, facilitating the degradation of pesticides, pathogens, and organic pollutants, thereby enhancing the overall water purification process. This dual approach not only safeguards the longevity and efficacy of RO membranes by preventing biofouling but also ensures that the water used in CEA meets the highest quality standards, devoid of both conventional and persistent contaminants.
The significance of this approach extends beyond water purification, aligning seamlessly with the principles of sustainability in agriculture. By optimizing water usage, minimizing waste, and reducing reliance on chemical fertilizers, the integration of AOPs and RO contributes to eco-friendly farming practices. This not only promotes the resilience and health of crops but also mitigates the environmental impact associated with agricultural activities.
Through the collaborative use of RO and AOPs in CEA, a robust foundation is established for water purity, nutrient control, and environmental sustainability. This ensures not only the success of contemporary agricultural practices but also reflects a conscientious approach toward mitigating environmental challenges associated with crop production.







